Structure of Ionic Compounds
Structure of Ionic Compounds: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Radius Ratio, Relation between Radius Ratio, Fluorite Structure & Antifluorite Structure etc.
Important Questions on Structure of Ionic Compounds
An ionic compound possesses type crystal structure. The coordination number of and ions in crystals of is:
A compound AB has rock salt type structure. The formula weight of AB is 6.023 Y amu, and the closest AB distance is nm, where Y is an arbitrary number. The density of lattice is
In which of the following crystals, the alternate tetrahedral voids are occupied?
The edge length of ( structure) is . Assuming contact along the cell edge, calculate the radius of ion
A student finds a crystal of having mass He uses some of it to prepare solution. How many unit cells are remained in the crystal ?
A crystal is made of particles and . A forms packing and occupies all the octahedral voids. If all the particles along the plane as shown in figure are removed, then, the formula of the crystal would be :
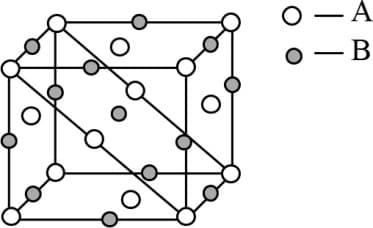
The coordination number (CN) of a ion in is . Hence, CN of is-
A solid compound has structure. If the radius of the cation is , the radius of the anion in pm will be
(Round of the answer up to four significant figures)
In solid, if all the ions are removed along one of the axes joining the centres of any two diagonally opposite edges in a unit cell, then the resulting stoichiometry of the solid is
The interionic distance between cation and anion in caesium chloride crystal will be :-
In crystal, the number of nearest neighbours of each ions are:-
An ionic solid crystallises in rock salt structure with density . If the radius of cation and anion is and respectively, then the molar mass of solid is
The radius of ion is and ion is . The co-ordination number of ion is:-
Which type of structure does have if ionic radii of and respectively are and :-
The tetrahedral voids formed by arrangement of ions in rock salt structure are
What will be value of in crystal having edge length ?
The positions of ions in structure are:
In a solid having the structure, atoms occupy the every and atoms are in . If all the face-centred atoms along one of the axes are removed, then the resultant stoichiometry of the solid is-
The edge length of face centred cubic unit cell having rock salt structure is . If the radius of the cation is the radius of the anion is-
